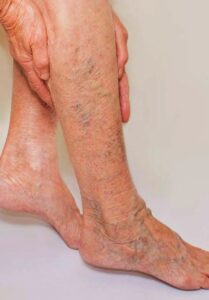
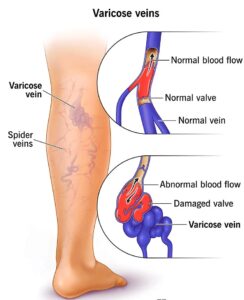
Varicose veins are swollen and twisted veins that are usually found just beneath the skin’s surface, most commonly in the legs. They occur when the valves in the veins that help blood flow back to the heart become weak or damaged, causing blood to pool in the veins and stretch them out.
SYMPTOMS OF VARICOSE VEIN
- Visible, bulging veins that are blue or purple in color.
- Aching or heaviness in the legs, especially after standing or sitting for long periods of time.
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet.
- Itching or burning sensations around the veins.
- Skin discoloration or ulcers around the affected veins.
- Throbbing or cramping in the leg
CAUSE
Varicose veins are caused by a weakening or damage to the valves in the veins that help blood flow back to the heart. When these valves don’t function properly, blood can pool in the veins and cause them to stretch and become enlarged.
There are several factors that can increase the risk of developing varicose veins, including:
- Age: As we age, the valves in our veins can become weaker and less efficient, increasing the risk of varicose veins.
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop varicose veins, possibly due to hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause.
- Family history: If other family members have varicose veins, it may increase the likelihood of developing them.
- Obesity: Excess weight can put additional pressure on the veins, making it harder for them to function properly.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and the increased pressure on the veins from the growing uterus can increase the risk of varicose veins during pregnancy.
- Prolonged standing or sitting: Jobs or activities that require long periods of standing or sitting can make it more difficult for the veins to move blood back to the heart, increasing the risk of varicose veins.
- Previous blood clots: A history of blood clots in the legs can damage the veins and increase the risk of varicose veins.
TREATMENT
Treatment options for varicose veins depend on the severity of the condition and the symptoms experienced. In some cases, lifestyle changes may be sufficient to alleviate symptoms, while in others, medical procedures may be necessary. Here are some common treatments:
- Lifestyle changes: Simple lifestyle changes such as exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, and elevating the legs can help alleviate symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening.
- Compression stockings: Compression stockings can help improve blood flow in the legs by applying pressure to the veins. They are available in different strengths and sizes and can be purchased over-the-counter or prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Sclerotherapy: In this procedure, a solution is injected into the affected vein, causing it to scar and close. Blood then reroutes through healthier veins.
- Endovenous laser treatment (EVLT): A minimally invasive procedure that uses laser energy to heat and seal off the affected vein.
- Vein stripping and ligation: In this surgical procedure, the affected vein is tied off and removed through small incisions. This is usually done under general anesthesia.
- Radiofrequency ablation: A minimally invasive procedure that uses radiofrequency energy to heat and seal off the affected vein.
- Ambulatory phlebectomy: A minimally invasive procedure that involves removing the affected vein through small incisions.
It is best to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment option for your individual case.
